The body of the body: examining the films of Lynne Sachs, inspired by a new retrospective.
https://brooklynrail.org/2024/07/film/DCTVs-Lynne-Sachs-From-the-Outside-In
July 1, 2024
By Hannah Bonner
In Barbara Hammer’s memoir HAMMER! Making Movies Out of Sex and Life she writes, “My films begin in what I call feeling images, an inseparable unity of emotion and thought/idea/image and internal bodily states of excitement.” Hammer’s desire to wed both emotion and thought, objects and bodies, could also be the epigraph to the experimental filmmaker and writer Lynne Sachs’s ongoing illustrious career. 2024 marks forty years since Sachs took her first video class at DCTV, where their June retrospective From the Outside In honors Sachs’s oeuvre of experimental shorts, cinepoems, and hybrid documentaries that explore feminism, family, New York City, labor, and “internal bodily states of excitement” with radical empathy and joy evinced in the act of their making.
From the Outside In features twenty-four films from Sachs’s body of work spanning 1983 to 2024, as well as an artist talk and workshop on uniting poetry with cinema. This preoccupation with language and translation—or the ever ongoing interplay between the aural, textual, and visual—is always at the forefront of Sachs’s work. In the very first program, “Performing the Real,” her short Fossil (1986) opens with a series of bodies in medium close-up performing various repetitive terpsichorean movements. The VHS camera, handheld, slightly unsteady, traces their shadows and gestures against the room’s white walls. Sachs then cuts to video footage of women in Ubud, Bali, packing sand into their baskets at a river bank. Through juxtaposition, the dance is both an interpretation as well as a translation of the Indonesian women’s labor. As Sachs elaborates in a recent phone interview, the cut is “another type of line break” that allows “the juxtapositions between shots … to have [what we’ll call] free song.”
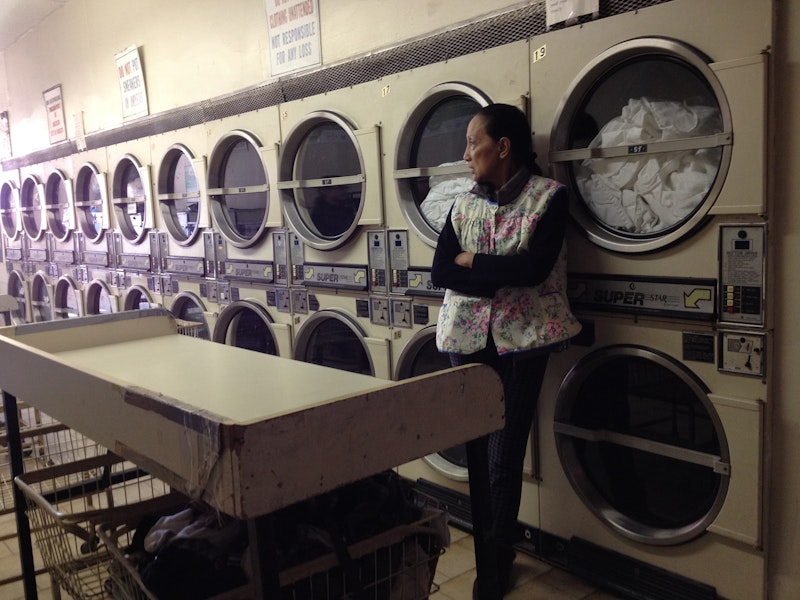
The Washing Society (2018) expands upon the content and form of Fossil. Sachs initially began this projectwith her co-director/playwright Lizzie Olesker by informally interviewing various people who worked in laundromats to create the play Every Fold Matters, which was performed in laundromats all over New York. The composite of all those different conversations is also the content of her film. In between subjects candidly sharing their experiences of racism or overtime at work, The Washing Society also features actors delivering monologues about laundering or dancers bounding atop site specific washing machines with interpretive abandon. The Washing Society makes visible typically invisible labor both by conducting talking head interviews, as well as by lovingly translating folding gestures into emotive dance. The mix of registers (veering from participatory to performative modes of hybrid documentary), coupled with the chorus of voices, creates a powerful panoply of experiences on this historically marginalized, gendered, and racialized labor.

Swerve concludes “Performing the Real’s” program by deftly (and movingly) uniting Sachs’s interests in translation, language, and text on screen. Inspired by Paolo Javier’s (Queens Poet Laureate 2010–14) sonnets in his 2021 book O.B.B. a.k.a. The Original Brown Boy, Swerve takes place in both an Asian food market and a playground in Queens. As various actors recite Javier’s lines, the camera tracks their movements closely like a confidant; at times, text layers the images, language equally worthy of sight as a face or a hand. Sachs further underscores her love of language in her short A Year in Notes and Numbers (2017) where the camera cuts from marginalia to to-do lists to vital signs in rhythmic succession. Sachs describes A Year as a “concise, autobiographical poem … made from the detritus. [It’s all] about the micro coming together.” Text typically delegated to the margins—or reserved solely for medical spheres—takes center frame.
Elsewhere, like in E•pis•to•lar•y: Letter to Jean Vigo (2021), the letter becomes another format from which to aurally and textually examine the power and politics of images. E•pis•to•lar•y begins with the white text “Dear Jean” against a black screen, ominously overlaid with the chatter of children and what sounds like a crackling fire. Sachs then cuts to black-and-white footage of the January 6th rioters descending on the Capitol before cutting back to the black screen where white text now states, “I don’t believe that childhood is swathed in innocence.” Each member of this mob was once a child—but children are equally capable of inciting chaos as adults. Sachs subsequently cuts to footage from Peter Brook’s Lord of the Flies (1963) as two young children push a large rock from a cliff. When the rock begins its descent, Sachs immediately cuts back to the rioters overturning a barricade; the objects, as well as the sound bridge of the rock falling, links the two disparate source materials. The result is a deeply unsettling collage of mob mentality that activates the viewer not just intellectually, but sensorially due to the match on action cuts and sound bridges. This is a film where the power of images surpasses the power of the written word. Through disquieting visual juxtapositions, Sachs’s E•pis•to•lar•y returns us to Hammer’s “inseparable unity” of embodied violence and political ideology.
Yet, politics—and the politics of identity—are never removed from any of Sachs’s work. She is always already attuned to bodies (both her own and others’), and their multiplicities, gradations, and variations. As Audre Lorde wrote, “It is not our differences which separate women, but our reluctance to recognize those differences and to deal effectively with the distortions which have resulted from the ignoring and misnaming of those differences”; Sachs’s films live by Lorde’s tenet that difference is worthy of record—and celebration. Some films, like Your Day is My Night (2013), include both English and Chinese subtitles; others, like Tip of My Tongue / En la punta de mi lengua (2017), include Spanish subtitles on screen. Sachs does not always automatically assume her audiences are English speakers. Nor is she interested in documenting a single political or social experience. Nowhere is such a chorus of voices more personally rendered than in Film About a Father Who (2020). Filmed over thirty-five years, Sachs’s portrait of her charismatic yet unknowable father incorporates interviews with family members who provide loving, albeit troubling, insight into Ira Sachs Sr. as a father, husband, lover, and son. As additional facts come to light, Father reveals that sometimes the best story is told by multiple people, not just one.
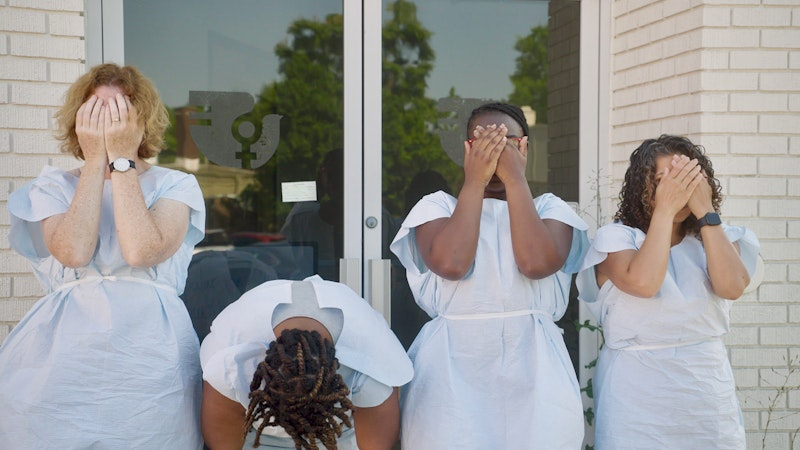
Contractions (2024)1, a much more performative documentary than Film About a Father Who, stages its bodies, rather than observes them. As an obstetrician and reproductive rights activist narrate their time working in an abortion clinic offscreen, various performers congregate outside a closed abortion clinic in Memphis, Tennessee in a long shot, their backs to the camera. The decision to obscure the faces of the performers is both to protect their privacy as well as to formally gesture to collective solidarity. Though the bodies range in age, race, and nationality, the choreography (and current political landscape) unite them in a post-Roe world, as does the cinematography which holds each and every body in the frame. Though we do not know every person’s individual story, Sachs’s camera does not discriminate. The long shot makes it possible that every person’s body, however anonymous, is seen.
The reproductive politics of Contractions (2024) recalls Sachs’s 1991 film The House of Science: A Museum of False Facts, a more formally embodied polyphonic collage film about women’s bodies. Incorporating archival footage as well as her own home movies, The House of Science is a scintillating examination of sexuality and science’s gendered biases. Whereas Contractions requires (necessarily so) a level of remove due to the anonymity of the actors, The House of Science is much more personal due to Sachs’s incorporation of her own story, as well as varied footage. On a formal level, I would argue Sachs’s works achieve Hammer’s “internal states of bodily excitement” when they are not as performative or tightly choreographed, but more interested in the power of montage, graphic matches, and the interplay between language and sound, because it is not just the actors, but the medium itself which activates new ways of seeing.

In The House of Science, Sachs’s diary chronicles receiving a diaphragm from “Dr. L.” in preparation for going to college, just as Esther Greenwood, in Sylvia Plath’s novel, receives a diaphragm to get out from under the bell jar’s oppressive dome. But Sachs’s doctor doesn’t tell her how to use it. Sachs’s text on screen elaborates:
My memory of being a girl includes a “me” that is two. I am two bodies—the body of the body and the body of the mind. The body of the body was flaccid and forgotten. This was the body that was wet with dirty liquids, holes that wouldn’t close, full of smells and curdled milk.
While Sachs may have once described her body as leaky and porous, full of “dirty liquids” and “smells,” her overall filmography affirms a heuristic approach to radical self-acceptance, not just of herself, but of others around her, including friends, family, and fellow artists like the aforementioned luminary Hammer. Through such ongoing generosity at both the level of content and form, Sachs’s films arouse ongoing intellectual and emotional compassion through myriad actors, materials, and mediums.
- Contractions will begin streaming in perpetuity on the NYT OpDocs page as part of their coverage of the second anniversary of the Supreme Court’s Dobbs decision to end a woman’s constitutional right to an abortion.